LUNG DISEASE
A group of lung diseases that block airflow and make it difficult to breathe.
Emphysema and chronic bronchitis are the most common conditions that makeup COPD. Damage to the lungs from COPD can’t be reversed.
Symptoms include shortness of breath, wheezing, or a chronic cough.
Rescue inhalers and inhaled or oral steroids can help control symptoms and minimize further damage.
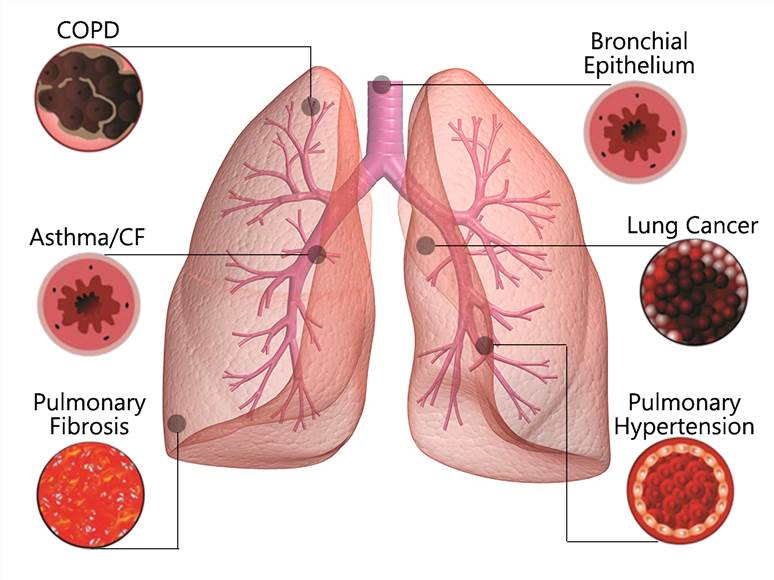
Lung Diseases Affecting the Airways
- Asthma. Your airways are constantly inflamed and may spasm, causing wheezing and shortness of breath. Allergies, infections, or pollution can trigger asthma symptoms.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). With this lung condition, you can’t exhale the way you usually would, which causes trouble breathing.
- Chronic bronchitis. This form of COPD brings a long-term wet cough.
- Emphysema. Lung damage allows air to be trapped in your lungs in this form of COPD. Trouble blowing air out is its hallmark.
- Acute bronchitis. This sudden infection of your airways is usually caused by a virus.
- Cystic fibrosis. With this condition, you have trouble clearing mucus out of your bronchi. This leads to repeated lung infections.
How to protect your lungs?
To increase your odds of avoiding chronic lung disease, consider these tips:
- Don’t smoke, or quit smoking. Avoid secondhand smoke.
- Try to reduce your exposure to pollutants in the environment, at work, and in your home.
- Exercise regularly. Aerobic exercise that increases your heart rate is best.
- Eat a nutritious diet.
- Get regular checkups with your doctor.
- Be sure to get a flu shot every year, and after you turn 65, get a pneumonia shot.
- If you’re at risk for lung cancer, ask your doctor about screening options.
- Test your home for radon gas.
- Wash your hands regularly, avoid touching your face, and stay away from individuals who are sick.
